BSNL (Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited) was incorporated on 1st October 2000 by the Government of India under the ownership of the Department of Telecommunications, Ministry of Communications. The largest government-owned wireless telecommunications service provider in India is headquartered in Delhi. The Chairman and Managing Director of BSNL is a government civil servant of the Indian Communication Finance Service or a central government engineer of the Indian Telecommunications Service.
As of February 2025, BSNL Mobile boasts a subscriber base of 91.01 million, ranking as the 4th largest mobile telecommunications network in India and the 25th largest globally. BSNL’s operating revenue grew by 7.8% in FY25, reaching INR 20,841 crore, compared to INR 19,330 crore in the previous year. Its total income also went up by 10% to INR 23,427 crore, up from INR 21,302 crore last year.
Although BSNL began strong and recorded profits for the first few years of its operations, it began recording losses after the year 2009. The company has recorded consistent losses in the last thirteen years of its operations. The company had reported a net loss of INR 5367 crore for the year ending March 31, 2024.
BSNL History
Why BSNL Failed | BSNL Downfall
Revival Efforts
BSNL Growth | Financials
Products and Services
BSNL Future Plans
Conclusion
BSNL History
BSNL owes its emergence to British India. It was the British who laid the foundation of the telecom network in India in the 19th century, establishing the first telegraph line in 1850 between Kolkata (erstwhile Calcutta) and Diamond Harbour. Within the next four years, the British East India Company laid telegraph lines across the country and opened the service to the masses in 1854. A year later, the British Imperial Legislative Council passed the Indian Telegraph Act.
Post India’s independence in 1947, the Post and Telegraph departments were bifurcated in the 1980s, and the Department of Telecom was established. The history of BSNL shows its rise as a major telecom player in the early 2000s, followed by a long period of decline due to competition and internal challenges.This eventually led to the emergence of government-owned telegraph and telephone enterprises, culminating in the foundation of BSNL.
Why BSNL Failed | BSNL Downfall

Founded at the turn of the century, BSNL successfully grew and expanded to reach annual revenues of approximately INR 40,000 crore in March 2007, compared to Airtel’s at INR 18,420 crore. Within the next two years, however, the PSU’s profits nosedived by 81% and its revenues fell by 6%. Since then, BSNL continued ailing year after year and by 31st March 2022 had incurred losses of INR 57,671 crore according to Devusinh Chauhan, Minister of State for Communication. By the end of October 2023, BSNL had experienced a cumulative loss of 21.4 million subscribers over 22 consecutive months, reducing its total subscriber count to just 92.87 million. The BSNL profit loss history reflects a sharp decline after 2007, with consistent losses accumulating over the years due to high costs and stiff market competition. The primary reasons for the continued downfall of BSNL are:
Tough Competition
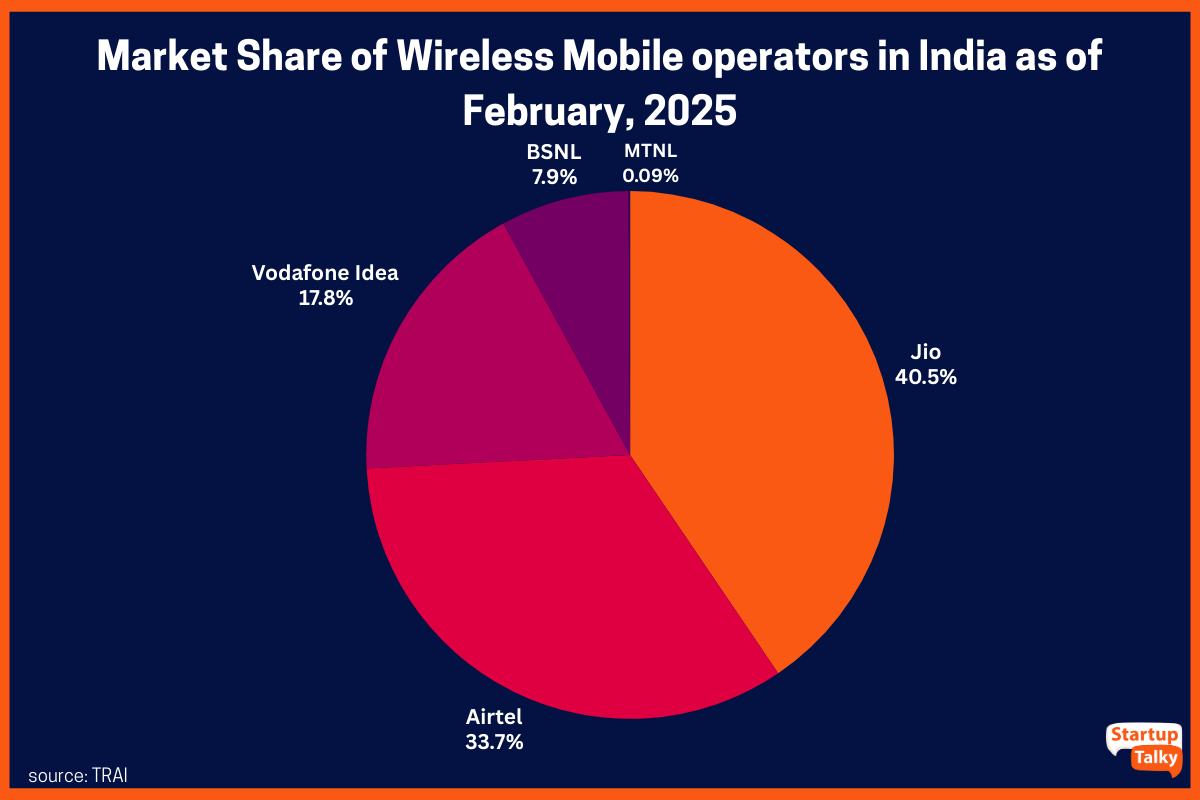
Commanding a 21% market share in 2005, similar to that of Bharti Airtel, BSNL began losing its ground in 2009 consistently, and by 2022, its market share had plummeted to a mere 7.9%. The rest 92% of the market was controlled by three major players – Jio, Vodafone Idea, and Bharti Airtel. The other major reason was the price war. Jio entered the telecom market with extremely cheap tariffs, forcing all private and public players to reduce their tariffs. BSNL, however, did not raise their tariffs with the subsequent increase by Jio and other players, resulting in a drop in their average revenue earned by users per month to INR 53 from INR 118. The BSNL failure is mainly due to slow decision-making, high employee costs, and tough competition from private telecom players.
Bureaucratic Function
Slow decision-making and a lot of red tape plagued the PSU. It eventually resulted in the company not being able to compete with private player competitors. Opposition from unions, failure to update equipment quickly, and repeated and unchecked government interference also played a significant role in BSNL’s decline.
High Employee Cost
While the company was battling the rising market competition, it was also plagued internally with high employee maintenance costs. This cost accounted for approximately 55% to 60% of the company’s expenditure.

Revival Efforts
The central government, in the past three years, has taken proactive steps to rescue the debt-ridden PSU from closing its doors permanently. Devusinh Chauhan, Minister of State for Communication, said that in October 2019, the Centre had approved a revival plan that included a reduction in employee costs through a Voluntary Retirement Scheme (VRS), debt restructuring by the raising of sovereign guarantee bonds, administrative allotment of spectrum for 4G services through capital infusion, monetization of core and non-core assets, and in-principle approval of the merger of BSNL and MTNL. He said, “As a result of these, BSNL and MTNL have become EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortisation) positive since the financial year 2020-2021.” The merger of BSNL and MTNL, however, has been delayed due to the former’s high debt.
By July 2022, the Centre approved a second revival package for BSNL of INR 1.64 lakh crore,, worth INR 1.64 lakh crore, aiming to upgrade the PSU’s services, allocate spectrum, de-stress its balance sheet, and augment aiming to upgrade the PSU’s services, allocating spectrum, de-stressing its balance sheets, and augmenting its fiber network by merging BBNL with BSNL. The BSNL growth rate has shown signs of improvement recently, driven by government support and network upgrades.
On June 7, 2023, the Union Cabinet approved the long-awaited third revival package for BSNL, valued at over INR 89,000 crore. With this approval, BSNL’s authorized capital has significantly increased from INR 1,50,000 crore to INR 2,10,000 crore. The Cabinet, chaired by PM Narendra Modi, has also granted BSNL a valuable allocation of 4G and 5G spectrum. These spectrum bands—700 MHz, 3,300 MHz, 26 GHz, and 2,500 MHz—are worth INR 46,338.60 crore, INR 26,184.20 crore, INR 6,564.93 crore, and INR 9,428.20 crore, respectively. BSNL’s goal is to expand 4G coverage to rural areas, offer high-speed internet through fixed wireless access (FWA) services, and support captive non-public networks (CNPN). This is indeed a major step forward for BSNL and the future of telecom services in our country.
“The first two packages brought BSNL out of a very difficult situation to a stable one. Now, BSNL should become a player that is able to bring connectivity to places where other commercial companies will not be able to go,” said Telecom Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw.
Examples of Revival
- Rural Connectivity Improving: BSNL upgraded its network in Himachal Pradesh under the BharatNet project and brought high-speed broadband to over 1,000 villages. This helped people access online education and health services.
- Strategic Partnerships: BSNL teamed up with tech companies like TCS to build its core 4G network. This shows its strong push toward modern technology. Despite past struggles, the BSNL growth rate is expected to rise with the rollout of 4G services and increased rural connectivity efforts.
- Customer-Centric Initiatives: By launching affordable prepaid plans, unlimited data offers, and free OTT subscriptions, BSNL has started winning back some of its old customers.
- Sustainable Operations: Through its VRS (Voluntary Retirement Scheme), BSNL reduced its staff by over 70,000 employees. This move greatly lowered its operating costs.
BSNL Growth | Financials

Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL) has reported a profit of INR 262 crore in the third quarter of the financial year, marking its first return to profitability since 2007. This milestone reflects the company’s focus on innovation, aggressive network expansion, cost optimization, and customer-centric service improvements.
Announcing the quarterly financial results, Shri A. Robert J. Ravi, CMD, BSNL, said:
“We are pleased with our financial performance this quarter, which reflects our focus on innovation, customer satisfaction, and aggressive network expansion. With these efforts, we expect revenue growth to improve further, exceeding 20% by the end of the financial year. Revenue from Mobility, FTTH, and Leased Lines has increased by 15%, 18%, and 14% respectively over Q3 of the previous year. Additionally, BSNL has successfully reduced its finance cost and overall expenditure, leading to a decline in losses by over INR 1,800 crore compared to last year.
To enhance our customer experience, we have introduced new innovations such as National WiFi Roaming, BiTV – Free Entertainment for All Mobile Customers, and IFTV for All FTTH Customers. Our continuous focus on Quality of Service and Service Assurance has further strengthened customer trust and reinforced BSNL’s position as a leading telecom service provider in India.”
The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has forecasted that state-owned Bharat Sanchar Nigam (BSNL) will achieve profitability in FY27, with an expected profit of INR 558 crore. This projection is based on anticipated revenue growth driven by the launch of 4G and 5G services in the coming years.
BSNL is expected to achieve a growth rate of 73.5% in revenue, from INR 19,344 crore in FY24 to INR 33,553 crore in FY27.
Products and Services
The government-owned entity provides both fixed-line telephones and mobile services on the GSM platform operating under the brand name CellOne and BSNL across the country.
BSNL Mobile
Offering prepaid and postpaid mobile services, BSNL Mobile also provides value-added services like Free Phone Service, India Telephone Card, Account Card Calling, Virtual Private Networks, Tele-voting, Premium Rate Service, and IPTV for its customers to enjoy television through the internet and VVOIP (Voice & Video Over Internet Protocol).
BSNL Landline
It was the only fixed-line telephone service that was launched in the early 1990s in the country. Only BSNL and MTNL, the other government-owned entity, were allowed to provide landline phone services in the country. BSNL and MTNL held 37.4 percent of the landline market share as of August 31, 2022, and 6.14 million users of BSNL in December 2023.
Internet
With approximately 7.5 lakh km of fiber-based telecom network across the country, it is the fourth largest ISP (Internet Service Provider) in India.
Broadband
The company’s broadband services include fixed-line and landline services using CDMA technology, providing internet access services through dial-up connections as prepaid, NetOne as postpaid, and DataOne as broadband.
Bharat Fibre
Launched in February 2019, Bharat Fibre offers IPTV, VoD (Video on Demand), VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol), AoD (Audio on Demand), BoD (Bandwidth on Demand), remote education, video conferencing services, interactive gaming, and Virtual Private LAN Services.
Bharat Net
In a revival effort, BSNL was merged with the government’s special purpose vehicle BBNL along with a package of INR 1.64 lakh crore. It gave the PSU an advantage of an additional 5.67 lakh km of optical fiber laid across 1.85 lakh village panchayats using the Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF).
4G Service
In January 2019, the public sector unit started the 4G services in a few cities and towns in the states of Bihar, Jharkhand, and Uttar Pradesh.
5G Services
BSNL CMD PK Purwar said in an interview that BSNL would begin 5G operations by 2025. Adhering to the Government of India’s ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’, its 4G and 5G networks are set to be completely home-grown Indigenous technology.
BSNL Future Plans
Here are the details of BSNL’s growth plan for network improvement:
- Moving to 4G Network: As part of the ‘Atma Nirbhar Bharat’ mission, BSNL plans to set up 100,000 4G sites across India. The 4G equipment will be ready for a future 5G upgrade. BSNL is also working on providing 4G services to villages that currently lack coverage.
- Network Upgrades: BSNL is upgrading its network with Super Edge Routers for its internet and 4G rollout. They are also planning improvements like a new Billing & Customer Care System, Universal SIM, Over The Air (OTA) updates, and Embedded SIM (eSIM). BSNL is also planning to install Remote Fiber Test Systems for better monitoring and testing of its network, as well as using All-Dielectric Self-Supporting Optical Fiber Cable. International long-distance connections will also be switched from TDM to IP.
- Broadband Upgrades: BSNL aims to make use of the Bharatnet infrastructure to improve internet access across India. They have started the BNG project to provide faster internet and are planning a MPLS-IP based Access and Aggregation Network (MAAN) to increase bandwidth and meet traffic needs.
- Cyber-Security: BSNL is implementing cyber-security solutions in its MPLS Gateway Network and secured web filtering to ensure a safer online environment.
Challenges Ahead
BSNL’s efforts to bounce back are commendable, but it still faces some challenges:
- Funding Needs: It needs ongoing investment to launch 5G and upgrade its network.
- Tough Competition: Competing with fast-moving private companies is not easy.
- Winning Back Customers: To regain customer trust, BSNL must keep improving its service quality over time.
Conclusion
Chauhan infused confidence in the PSU by saying, “With the implementation of these measures, BSNL is expected to turn around and become a profit-earning entity.” BSNL’s journey, by no means, has been easy. Its profit-making operations quickly took a sharp downturn due to reasons that were, probably, avoidable. However, with the Central Government’s strong backing, the PSU is set to make a stronger comeback than before.
FAQs
Who is BSNL owner or founder?
BSNL (Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited) was incorporated on 1st October 2000 by the Government of India under the ownership of the Department of Telecommunications, Ministry of Communications. BSNL is a 100% Govt. of India-owned Public Sector Undertaking with an authorized share capital of Rs. 1,50,000 crores. Government of India is the owner of BSNL.
What is the net worth of BSNL?
The net worth of BSNL as of 31 March 2024 is INR 106625 crore.
Is BSNL all over India?
BSNL Mobile has a pan-India presence with a presence in all 22 telecom circles in India. It is the fourth largest mobile network operator in India.
Who owns BSNL?
BSNL is owned by the Government of India.
Is BSNL planning to launch 5G?
BSNL CMD PK Purwar said in an interview that BSNL would begin 5G operations by 2025.
How does the revival package affect BSNL’s authorized capital?
The third revival package has increased BSNL’s authorized capital from Rs 1.50 lakh crore to Rs 2.10 lakh crore.
Which is the cheapest mobile recharge plan of BSNL?
The minimum BSNL validity recharge is 15 days at ₹36. This recharge plan will give you free calls, data, and SMS at the lowest cost.
What is BSNL growth in last 10 years?
BSNL has incurred significant losses over the last 10 years, with a cumulative loss exceeding ₹1,800 crore in FY23.
Why did BSNL fail?
BSNL failed due to slow upgrades, high costs, and strong competition from private telecom companies.






