Urban Company, previously UrbanClap, has made our at-home services so easy. It has revolutionized the way we use our various services.
Earlier, we had to go out to get our services done. But with Urban Company, we get to enjoy them at home. The services include beauty, spa, repair work, cleaning, and more.
It aims to provide authentic and affordable services to the users. To enable these home services and manage the processes, the company possesses a great business model. Its model ensures the connectivity of skilled professionals with service users.
Urban Company is making its stock market debut on September 17, 2025, on the BSE and NSE, following the completion of its IPO allotment on September 15.
Let’s look at the business model of Urban Company, the company that involves proper planning, management, and business strategies. This helped them become one of the most popular startups.
About Urban Company
Founders and Team
Urban Company Business Model
The Business Model of Urban Company | How Urban Company Works
How does Urban Company Make Money | Urban Company Revenue Model
What are the Main Resources of Urban Company
About Urban Company
The company, founded in November 2014, is a home services company. The Urban Company came into existence to connect local services with technology. It enables the customers to get their required services at home.
Founders and Team

The masterminds behind this startup are Varun Khaitan, Raghav Chandra, and Abhiraj Bhal. They co-founded the company with an early-stage budget of INR 10 lakhs.
Varun Khaitan
Varun Khaitan is an IIT Kanpur alumnus who completed his B.Tech in Electrical Engineering and then went on to join Qualcomm as an Engineer. Leaving Qualcomm, Khaitan joined The Boston Consulting Group, where he served as an Associate and a Consultant. After serving the role for more than 2 and a half years, Khaitan left the company and started up with Urban Company.
Raghav Chandra
Raghav Chandra, another co-founder of Urban Company, served as a Software Engineer at Twitter before founding Urban Company, teaming with the other co-founders. Raghav has also founded another company, Buggi, in the interim. Raghav has interned in a series of companies, including Roamware, Infosys SETLabs, UC Berkeley, and Yelp Inc., after completing his BS in Computer Science and Engineering from the University of California, Berkeley.
Abhiraj Singh Bhal
Abhiraj Bhal is another co-founder of Urban Company. Bhal also has a background in Engineering, and that too in Electrical Engineering from IIT Kanpur, much like the previous co-founder. After completing his graduation, Abhiraj opted for an MBA in Business Administration from IIM Ahmedabad. He first joined as a Consultant at The Boston Consulting Group, where he served in the role of Consultant for 3 years. After quitting, he co-founded Urban Company.

Operating Areas
The Urban Company, founded in 2014, is the largest at-home services company in India and the UAE. The company operates in Dubai, Abu Dhabi, Sydney, Singapore, and fourteen cities in India.
Services and Audience
The Urban Company provides over 100 services now. These include beauty, grooming, cleaning, repairs, home educators, fitness trainers, and many more.
This new-age startup has a solution for almost all our services with one click. These various services have enabled the company to have a broad audience overall.
The main idea of the startup was to enable people to hire any service from the comfort of their homes. Indeed, it is doing a great job and has shown amazing growth.
The Urban Company has made a big name for itself in the service industry. It has developed an amazing amount of reliability among the customers.
By looking at all this, a few questions come to our minds. For example, how did a startup that started with a mere INR 10 lakhs grow so much? In this uncertain era, how are people even trusting the platform?
All such questions have a simple answer. It is the company’s simple yet super-effective business model backed by huge investments.
The company launched another service in 2022, where it would be offering free medical consultation, focusing on the hair and skin problems of women. As per the reports, Urban Company onboarded some dermatologists to give free medical counseling in a few Indian cities. Renowned cosmologist Dr Amit Karkhanis has been roped in by Urban Company to head its medical team.

Urban Company Business Model

The Urban Company has a straightforward business model. This is to connect the customers with their required services at home. The company helps you to bring in beauticians, fitness trainers, educators, electricians, plumbers, photographers, and many more.
It is a full-stack startup that uses algorithms for automated matchmaking. To make the platform more trustworthy, the company ensures public safety. The company performs background checks and also police verification of all the service providers.
The Urban Company is growing and gaining customers’ trust with its two-fold business model.
The Business Model of Urban Company | How Urban Company Works
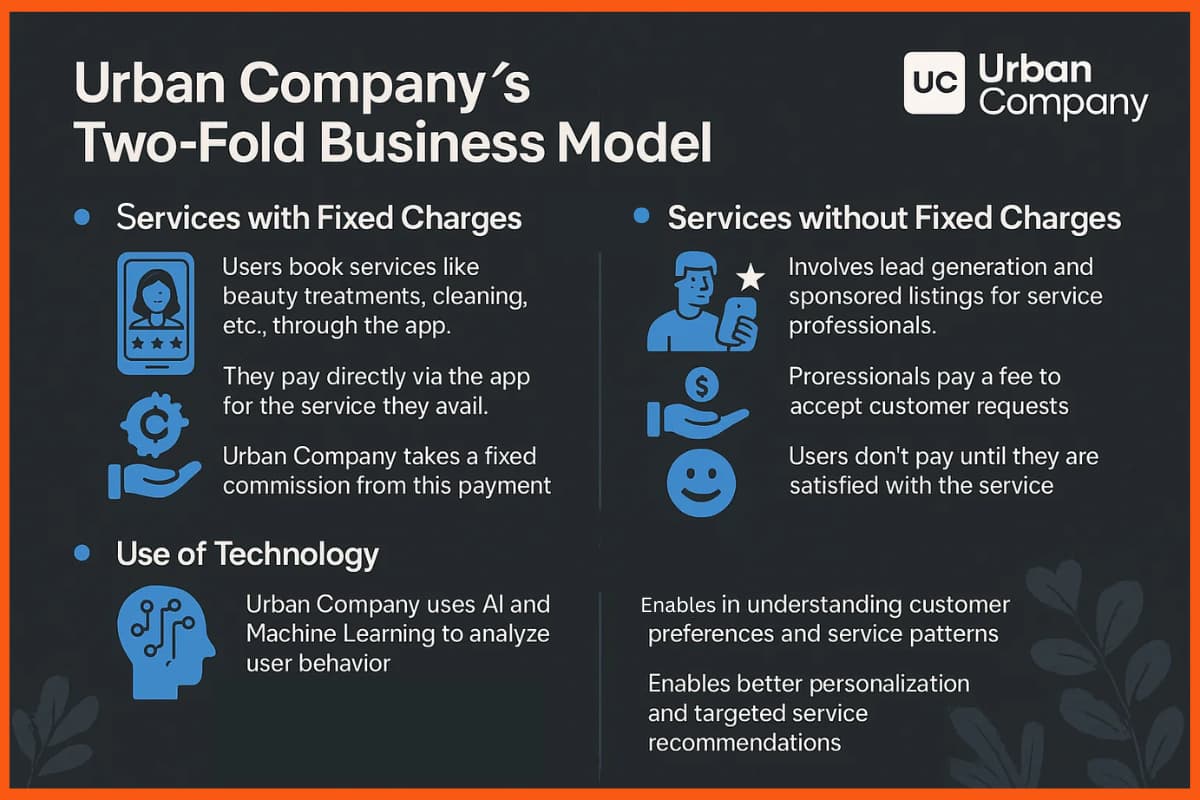
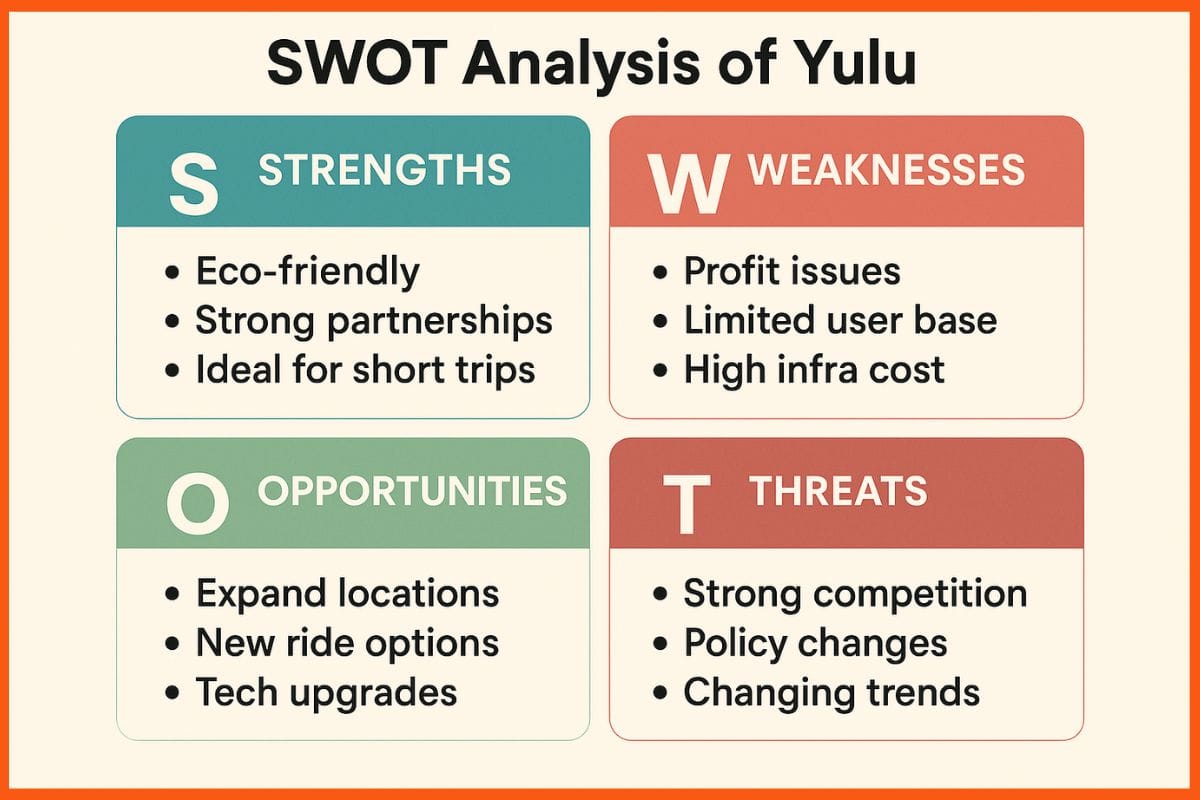
The Urban Company works on a two-fold model. This involves:
Services with Fixed Charge
Whenever a person uses the services of hiring a beautician, cleaner, or anything, they get charged through the app. It means they pay for the availed services through the app.
In this way, the company takes a fixed commission from this revenue.
Services without the Fixed Charges
There is a lead generation and sponsored listing. For this, the company charges the experts. The company makes sure that the users do not have to pay till they are satisfied with the services.
There is a process. In this, at first, the service providers have to pay a fee to accept the customer’s request. If the professional can satisfy the user and get paid for the services, then the monetization will be worth it.
Therefore, the urban company has created a successful business model for itself. It has begun to use the technology of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. This helps the app discover data insights and patterns of the users. This, after all, helps the company to know its customers’ needs better.

How does Urban Company Make Money | Urban Company Revenue Model
Urban Company’s revenue model comprises four key methods for generating income:
Commissions
Urban Company generates the majority of its revenue from subscription fees. They employ a commission-based model, charging a percentage of the service’s total price to the business owner. This approach ensures swift and dependable service for all customers. Urban Company determines specific commissions from each vendor or service provider based on their respective tasks. Thus, the more services they perform, the greater the rewards they receive for providing home services.
Lead Generation
Urban Company primarily earns revenue through commission charges, with lead generation as a secondary income stream. In the lead generation process, customers outline their needs, and the platform suggests suitable service providers. Customers can then directly contact these experts or be contacted by them. This approach facilitates connections between service providers and customers. As a result, Urban Company charges professionals and service providers for lead generation opportunities.
Reverse Auction
Service providers have the option to invest a fixed amount in promoting their skills through the Urban Company platform. In return for this investment, the company assists service providers in enhancing their conversion rates and generating leads.
Ads or Commercials
In addition to the previously mentioned revenue streams, another avenue for generating income is through advertisements. Various big businesses and manufacturers run their ads on the company’s platform. The company thus gets a fee in exchange for this.
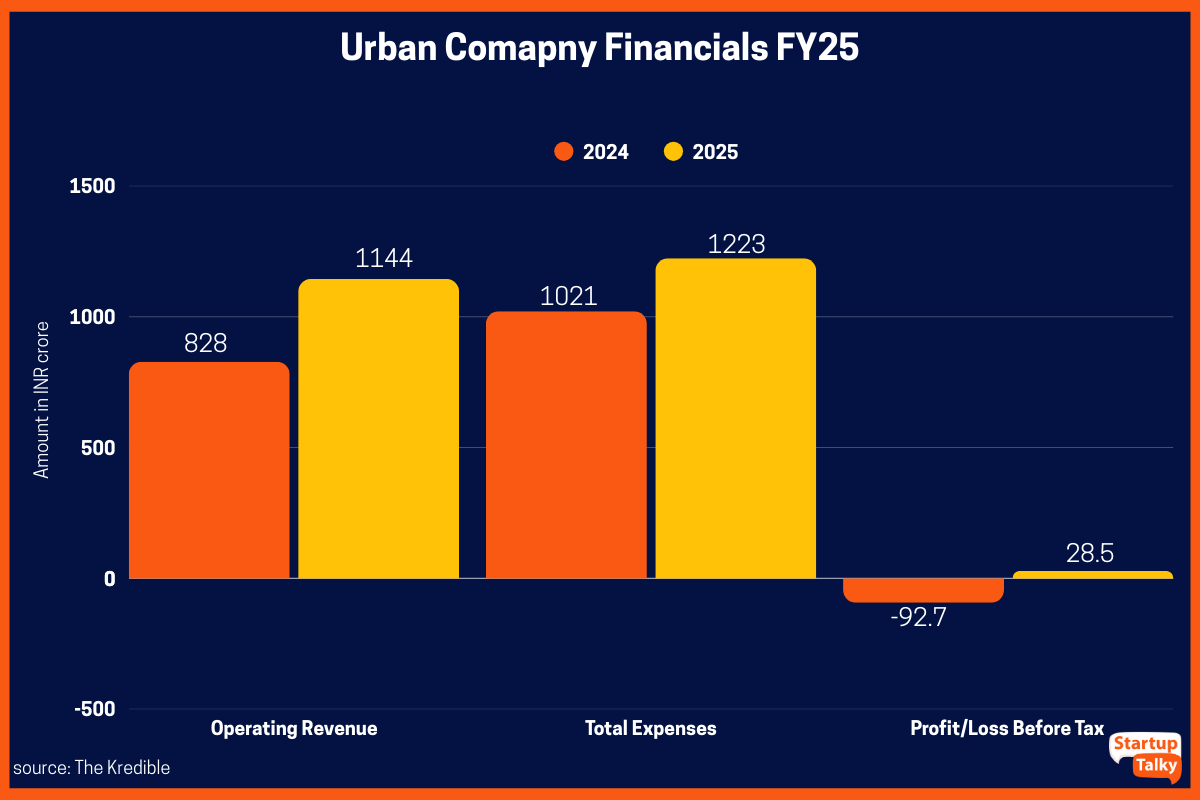
| Urban Company Financials | FY25 | FY24 | FY23 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue from operations | INR 1,144.5 crore | INR 827 crore | INR 636.6 crore |
| Total Expenses | INR 1,223.47 crore | INR 1,020.8 crore | INR 1,038.9 crore |
| Profit/Loss | INR 28.5 crore | Loss of INR 92.8 crore | Loss of INR 312.5 crore |
Urban Company has been on quite a growth journey! In FY25, Urban Company reported revenue from operations of INR 1,144.5 crore, up from INR 827 crore in FY24 and INR 636.6 crore in FY23. Its total expenses stood at INR 1,223.47 crore in FY25, compared to INR 1,020.8 crore in FY24 and INR 1,038.9 crore in FY23. After years of losses, the company turned profitable in FY25, posting a profit of INR 239.8 crore, against a loss of INR 92.8 crore in FY24 and a loss of INR 312.5 crore in FY23.
Urban Company has raised around US$560 million across 14 funding rounds so far. In September 2025, Urban Company raised US$56.7 million in a Pre-IPO round from investors including SBI Mutual Fund, Permira, Prosus, and Elevation Capital. The company recently became a unicorn, reaching a $2 billion valuation.
What are the Main Resources of Urban Company?
There are two main and most important resources of the Urban Company. The first is their official website. The second is their application, which is available for both Android and iOS.
The resources are made with similar technologies. These help the company in lead generation, promotions, and knowing the customers better.

Conclusion
The Urban Company has created a huge name for itself in the market. It made this possible because of its simple yet effective planning. The company did not make a complex business model for itself in the beginning, and it intends to keep it that way only.
This model helps to bring in cleaners, yoga trainers, educators, electricians, and many more. One can do all this from the comfort of one’s home with one’s smartphone.
The Urban Company’s business model aims to make the connectivity between customers and service providers faster and more efficient.
FAQs
What is Urban Company?
Urban Company is an Indian-based technology company that operates a platform connecting customers with a wide range of home services and skilled professionals. Founded in 2014, it offers services such as beauty and wellness, home cleaning, repairs and maintenance, fitness, tutoring, and more.
What is the business model of Urban Company?
Urban Company connects users or service seekers to service providers for daily services. The service list includes beauty, grooming, cleaning, repairs, home educators, fitness trainers, and many more.
What is the revenue model of Urban Company?
Urban Company’s revenue model comprises four key methods for generating income, which are from commissions, lead generation, reverse auction, and ads or commercials.
How Urban Company works?
Urban Company offers a platform that connects skilled and experienced professionals with users seeking specific services.
How to get an Urban Company franchise?
Urban Company doesn’t follow a traditional franchise model where individuals own and run physical stores. Instead, it operates a platform-based model where independent service professionals—like beauticians, cleaners, and plumbers—register on the app and offer their services directly to customers through the platform.
What is the business of Urban Company?
Urban Company is an online marketplace for home services where customers can book beauty, cleaning, repair, and maintenance professionals through its app/website.
What is Urban Company owner name?
Urban Company was founded by Abhiraj Singh Bhal, Varun Khaitan, and Raghav Chandra.
Urban Company is from which country?
Urban Company is based in India, with its headquarters in Gurugram (Haryana), India.